The RNAME provides the Search, Browse options. In order to make sure RNAME is convenient to be used, the help page is prepared.
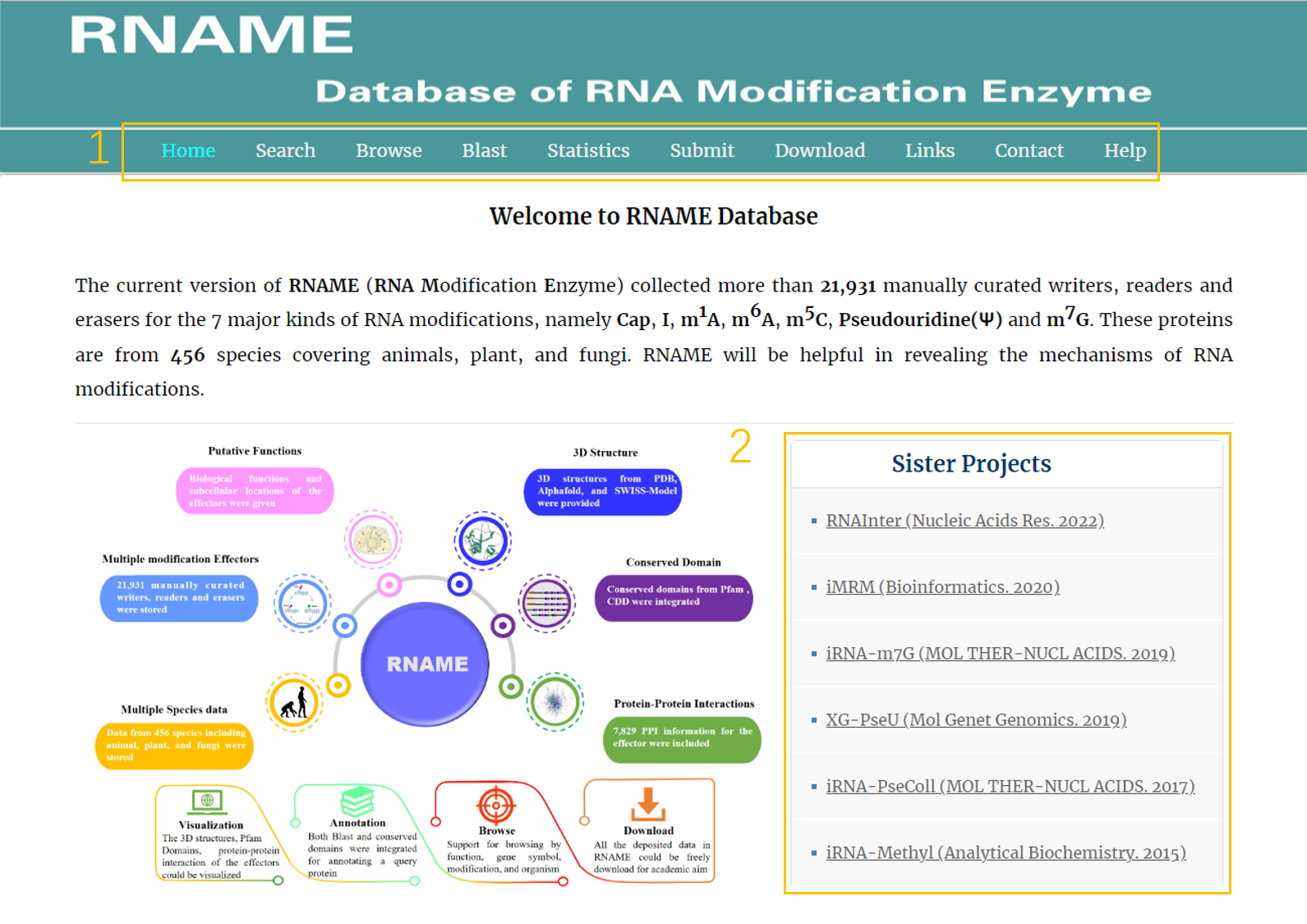
The homepage is displayed in the following:
1. Main functions of the database are provided in menu bar form (boxed in light orange).
2. Other projects contributed by our group (boxed in light orange).
Both exact, fuzzy search and batch search were supported
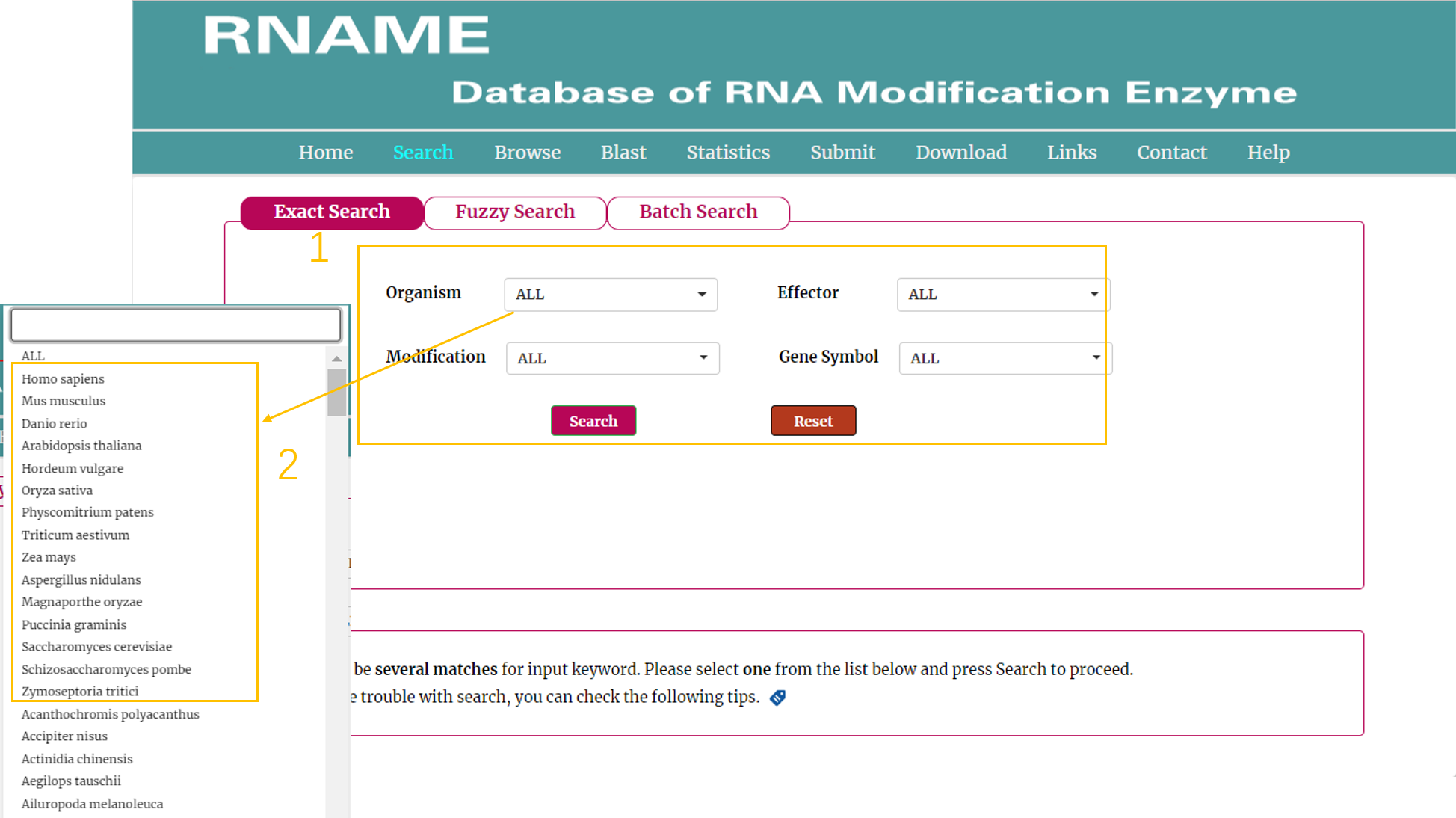
The Exact search page:
1. Four categories provided to search the database: "Organism", "Modification Type", "Effector" and "Genesymbol" in the dropdown menu as the keyword. After inputting the search item (such as homo sapiens) related to the concerned keyword and clicking the search button, the results will be shown in a new page.
2. For the "Organism" category, the top favorite species are provided for easy searching.
The Fuzzy search page:
1. For the Fuzzy Search module, users can choose the "Organism", "Modification Type", "Effector" and "Genesymbol" in the left panel as the keyword. Once the keyword was determined, users could enter the keyword according to the keyword type selected in the right panel. After selecting the item related to the concerned keyword and clicking the search button, the results will be shown in a new page.
2. Use NCBI Taxonomy to normalize your Organism information.

The Batch search page:
1. Select a dataset for your keywords.
2. Enter the keywords or upload a file.

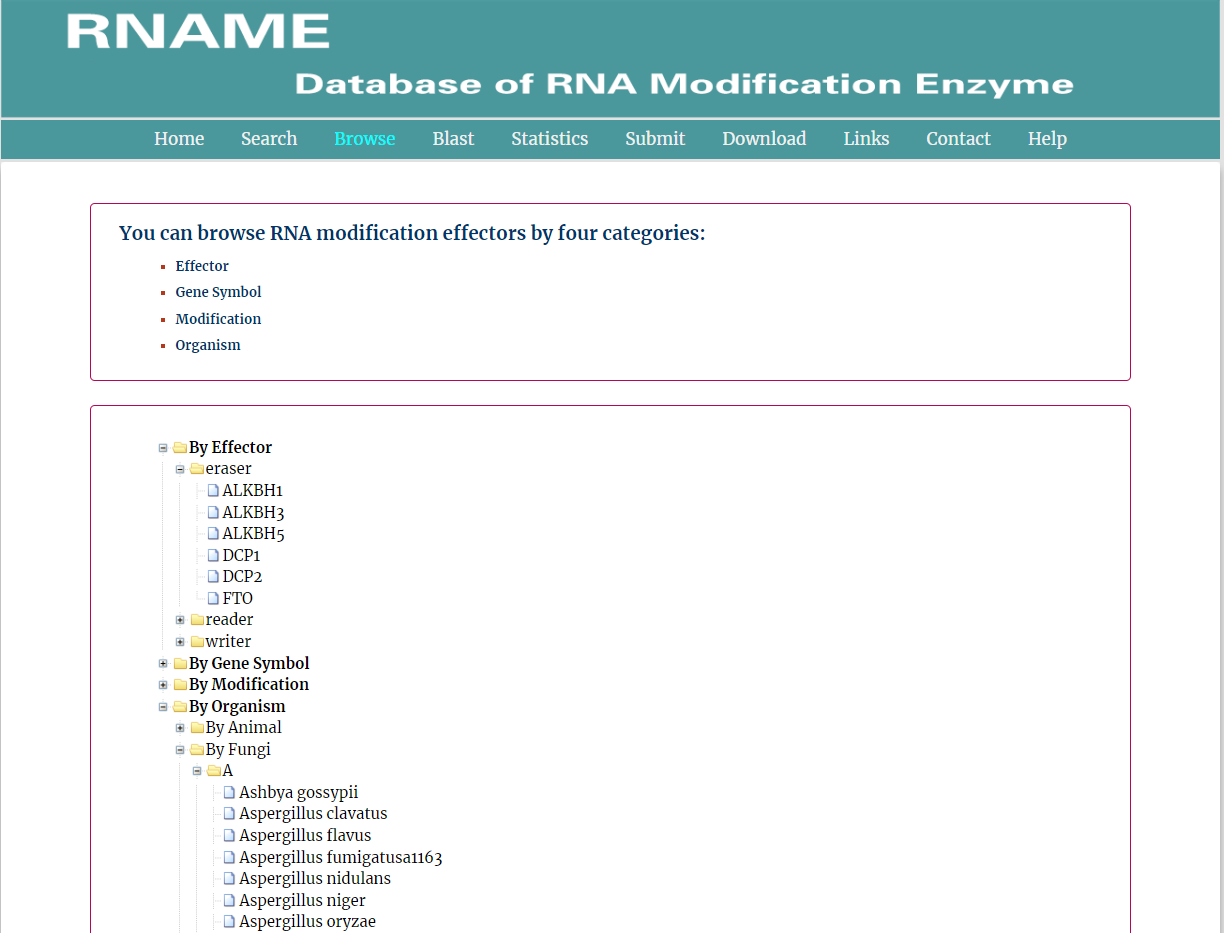
In the Browse page, users can browse the database according to Effector, Genesymbol, Modification, Organism, respectively. Once clicking the items under each category, the results will be shown in a new page.
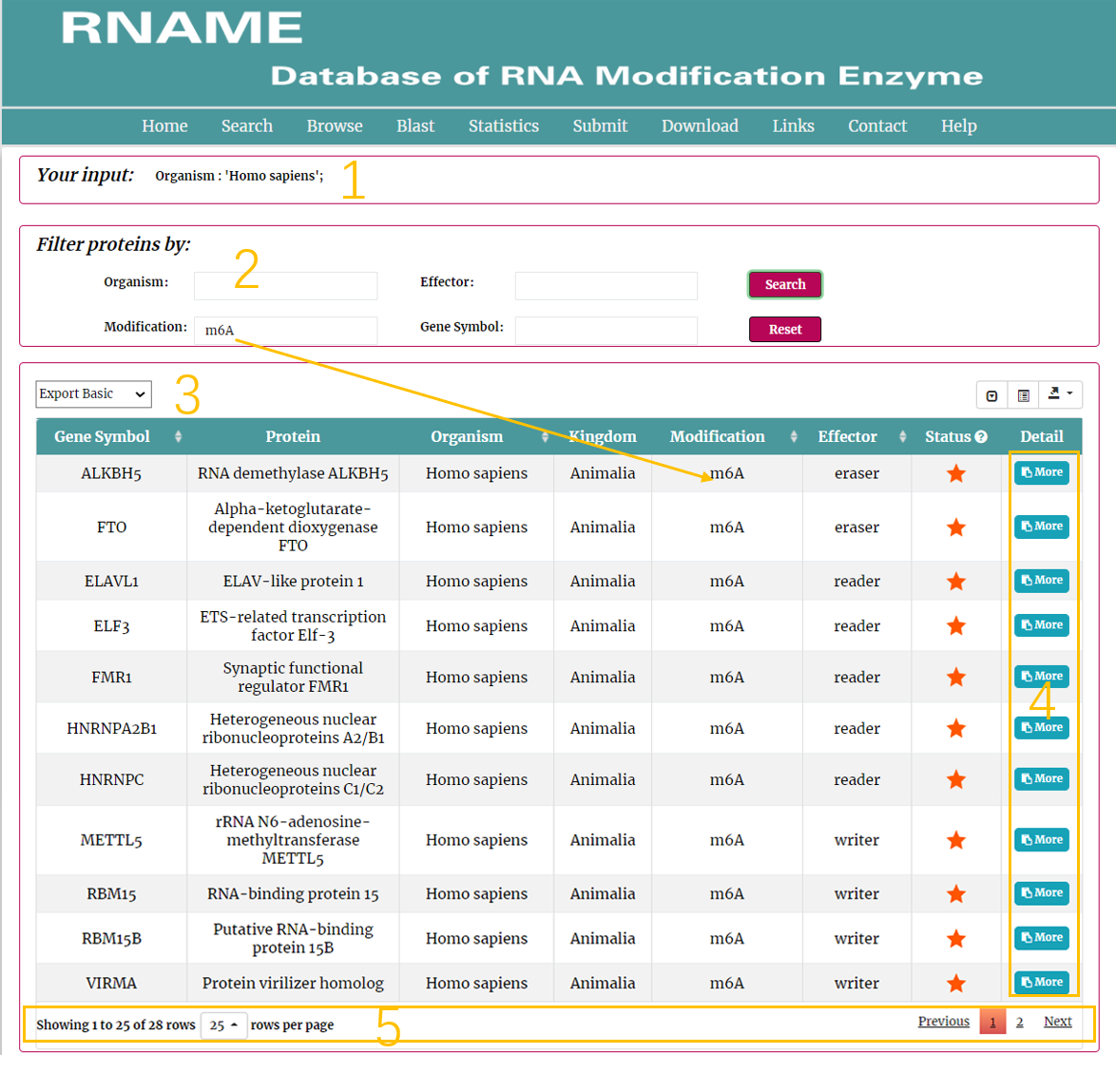
In the result page, all entries are listed with basic information including Enzyme, Protein, Organism, Kingdom, Modification, Effector, Status.
1. Current input conditions.
2. Filter the results.
3. Result list.
4. Click to link to detail page.
5. Click to turn the page.
Firstly, users can get basic information (Fig.5-1).
Basic Information:
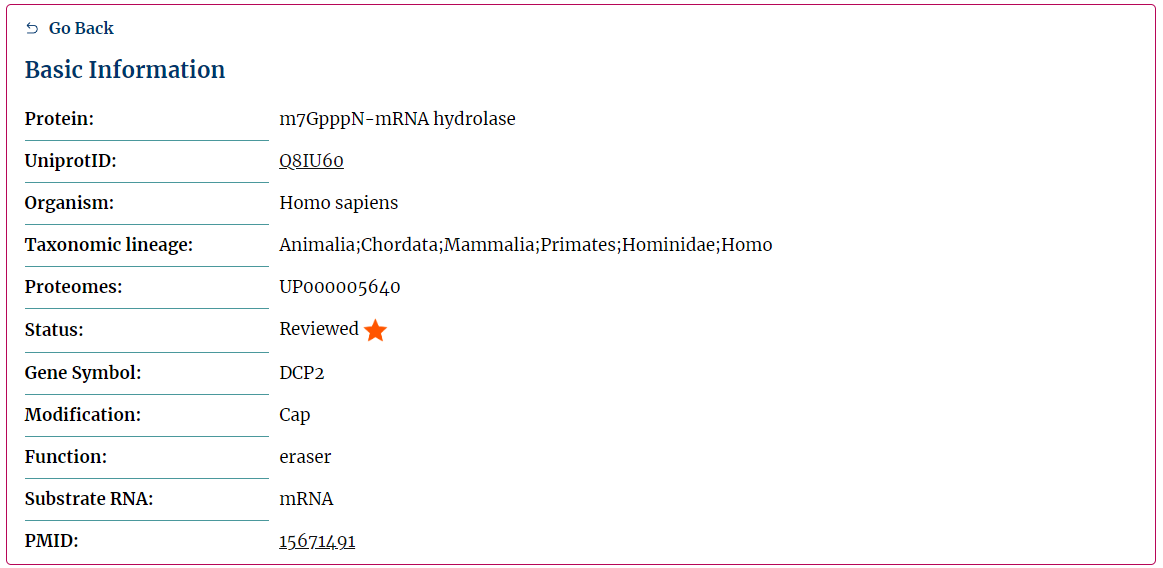
Fig.5-1 basic information
Secondly, users can get the structure of the protein (Fig.5-2).
Structure Information:
1. The sequence of the structure.
2. The structure.
3. The source of the structure. There are three sources of structure in this database: Alphaflod, RCSB-PDB, SwissModel.
4. Click to show structure.
5. Click to link to the Source.
6. Click to download the pdb file.
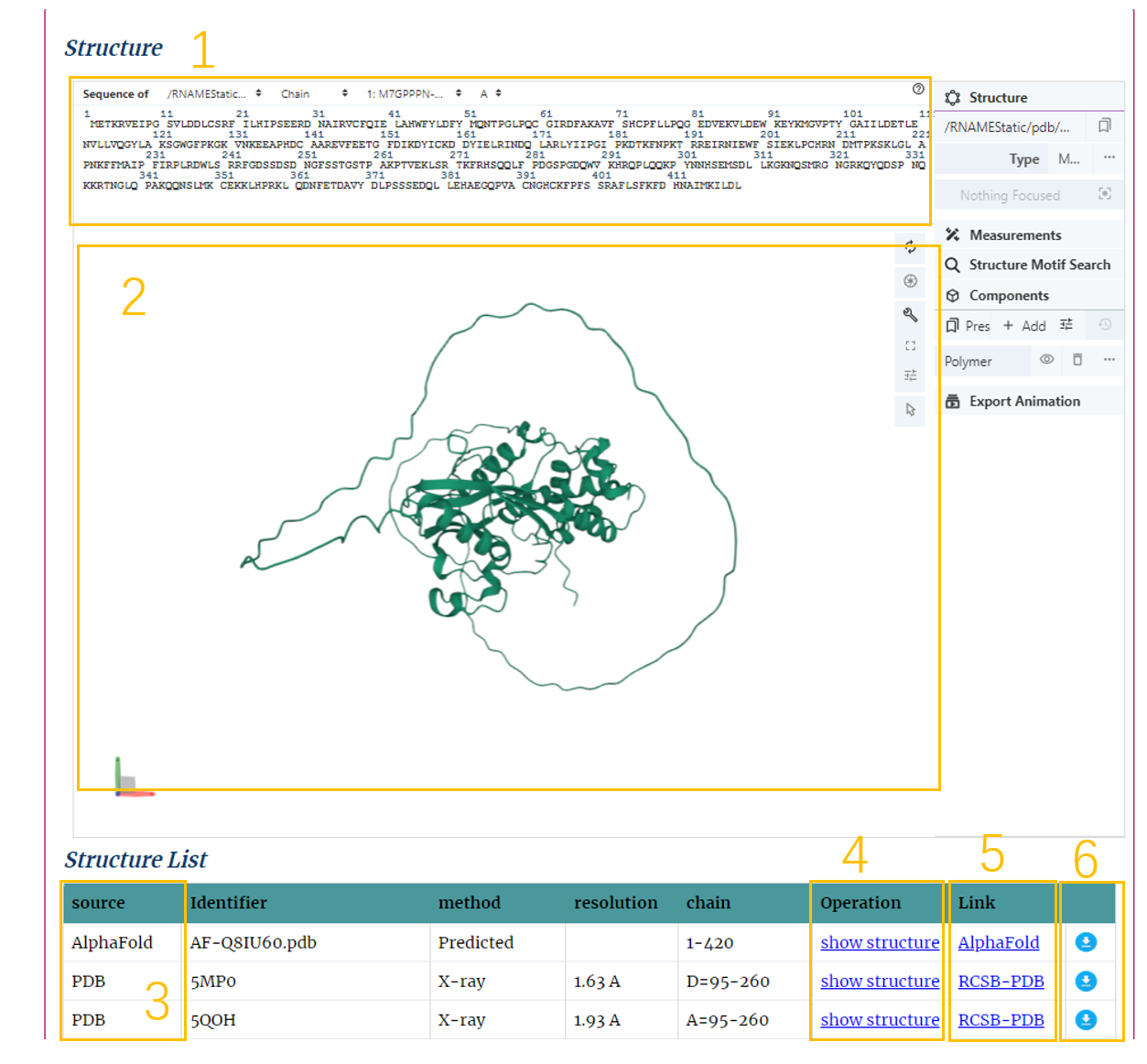
Fig.5-2 struture
Thirdly, users can get the protein-protein interaction network if the protein have (Fig.5-3).
Protein-Protein Interaction Information:
Select the top ten PPI from the String database

Fig.5-3 PPI
Fourthly, users can get the domains of the protein (Fig.5-4).
Domain Information:
1. This image shows the arrangement of the Pfam domains on this sequence. Click to show the domain information in the corresponding database.
2. E-values are based on the Pfam database or based on the Batch CD-Search.
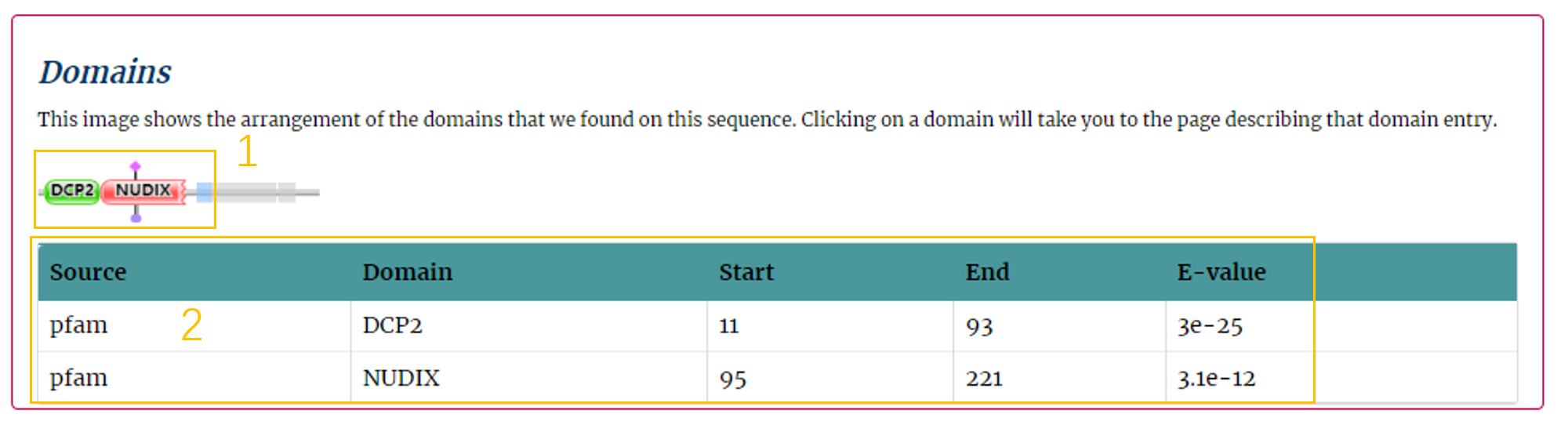
Fig.5-4 Domain
Fifthly, users can get the subcellular location of the protein (Fig.5-5).
Subcellular Location:
1. The subcellular location are based on the Uniprot Database or predicted by the Bioinformatics tool named SherLoc2.

Fig.5-5 Subcellular Location
Sixthly, users can get the function if the protein have (Fig.5-6.1 ).
Seventhly, users can get the genome annotation information of the prote (Fig.5-6.2).
Eighthly, users can get the sequence information of the protein (Fig.5-6.3).
Multiple Information:
1. The function information based on the Uniprot database.
2. The genome annotation databases.
3. The sequence information.

Fig.5-6 Multiple Information
In this page is for some other researches related to RNA modification
1. Other researches contributed by our group.
2. Researches related to other groups.